Medical Cannabis for IBD and Crohn’s Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease, or IBD, consists mainly of two conditions: Crohn's disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Both involve an autoimmune response where the immune system attacks healthy tissue causing inflammation. Over 1.6 million people in the United States suffer from IBD. There is no known cure for IBD, and many patients will suffer with symptoms for decades.
We know cannabis to have immune regulating and anti-inflammatory properties with little to no toxic effects. Based on the anecdotal evidence seen in medical dispensaries and the current scientific evidence, cannabis products should be considered in these patients and further research needs to be funded.
Watch our Video on Medical Cannabis and GI Disorders to Learn More!
Treating IBD: Know the Components of Cannabis
THC - Tetrahydrocannabinol
Cannabis contains chemicals called cannabinoids that interact with the human body’s natural endocannabinoid system. More research is needed, but here is significant scientific evidence supporting the use of Cannabis for IBD. Researchers have found abnormalities of the endocannabinoid system within the biopsy samples of patients with severe intestinal disease. These samples showed altered levels of endocannabinoids and/or CB receptors.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is one of the two major cannabinoids. In a small placebo controlled trial, published in 2013, looked at 21 Crohn’s patients who did not respond to therapy with steroids, immunomodulators, or anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. This study focused on an 8 week trial of inhaled Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, or Delta-9-THC. 5 of the 11 subjects in the THC group achieved complete remission. 3 of the patients were weaned from steroid dependency, and patients receiving cannabis reported improved appetite and sleep, with no significant side effects.
CBD - Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol or CBD is the other major cannabinoid. CBD has been shown to decrease inflammation. Several animal studies have shown CBD may decrease intestinal inflammation. However, other studies have demonstrated a cannabis extract containing high levels of CBD to be more effective than CBD alone. Such extracts have shown decreased intestinal damage from colitis and reduced hypermotility in a 2016 animal study.
Minor Cannabinoids
In addition to THC and CBD, over 130 minor cannabinoids have been identified, and several have shown promise in reducing IBD and inflammation symptoms. CBG is just one example. CBG is the third most common cannabinoid. A 2013 study demonstrated that CBG attenuated colitis in mouse studies, and the researches recommended that CBG should be considered for clinical experimentation in IBD patients. Anecdotally, many of our IBD patients report better health outcomes with products containing CBG.
Choosing Dosage Forms
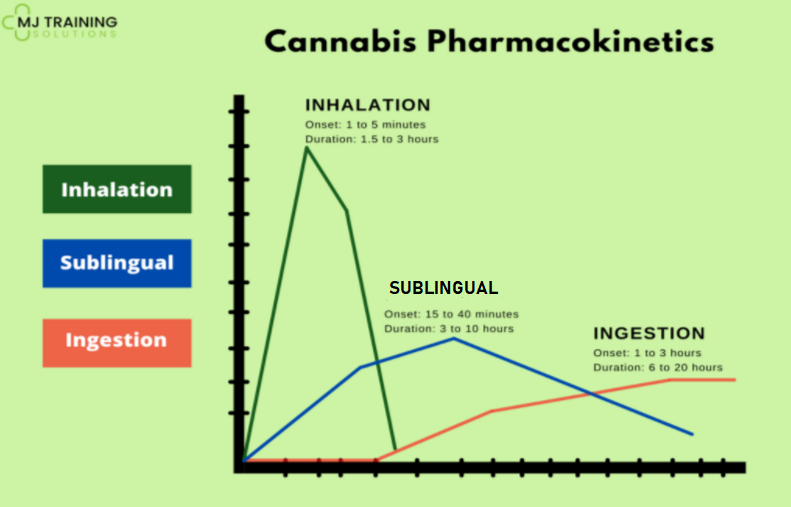
The different dosage forms of Cannabis have different onsets, delays, and durations. Combining dosage forms can be more effective.
RSO is produced by a very simple extraction, and it is not nearly as purified as some other cannabis products. Although it is rare for cannabis companies to test for flavonoids, it is likely that simply extracted RSO may contain more of these natural chemicals. Flavonoids show promise in fighting chronic inflammation and certain cancers.
There are several longer-acting dosage forms available, including tinctures and capsules. However, our Crohn’s patients seem to respond best to RSO, also known as Rick Simpson oil, which is a black and tarry substance that usually comes in an oral syringe. RSO can be tricky to dose. Some patients will squirt it out onto a cracker, cookie, or piece of candy. A normal dose of RSO is roughly the size of a grain of rice.